- Reading time:
- 10 minutes
Share this post

What Is COBOL Modernization? (All You Need to Know + Best Practices)
16 February 2026

Richard Katona
Head of Product Delivery
COBOL still runs mission-critical systems across banking, insurance, and government, but its age and complexity make updates risky and costly without the right strategy. This article breaks down what COBOL modernization means, why it’s crucial today, and how organizations can approach transforming legacy systems to improve scalability, integration, and maintainability while protecting core business logic.

Quick Summary
COBOL modernization helps organizations reduce operational risk while improving agility. This guide explains what COBOL modernization involves, the main approaches, and best practices for updating COBOL systems without breaking core business logic. You’ll also see how Kodesage supports modernization through automated documentation, system mapping, and clear system insights.
The Growing Challenge of Maintaining COBOL Systems
COBOL still powers critical systems in banking, insurance, and government, adopted for its reliability and ability to process high-volume transactions on mainframe systems. While these systems continue to work, they are complex, underdocumented, and risky to change; even a small update can cause outages or disrupt operations.
Today, those same systems are harder to manage. Experienced COBOL developers are retiring, modern integrations are difficult to implement, and security and compliance expectations are higher than ever. Organizations now need a way to modernize safely, without losing the business logic these systems still depend on.
This Kodesage article explains what COBOL modernization is, why it's crucial now, and how organizations can modernize step-by-step while preserving business logic, improving agility, and reducing risk.
What is COBOL modernization?
COBOL modernization is the process of transforming COBOL-based systems, often built decades ago, to meet modern architectural, operational, and business requirements.
Modernization can take many forms. Teams may refactor existing code, expose COBOL logic through APIs, migrate workloads to the cloud, or move mainframe-based applications to more flexible, scalable environments.
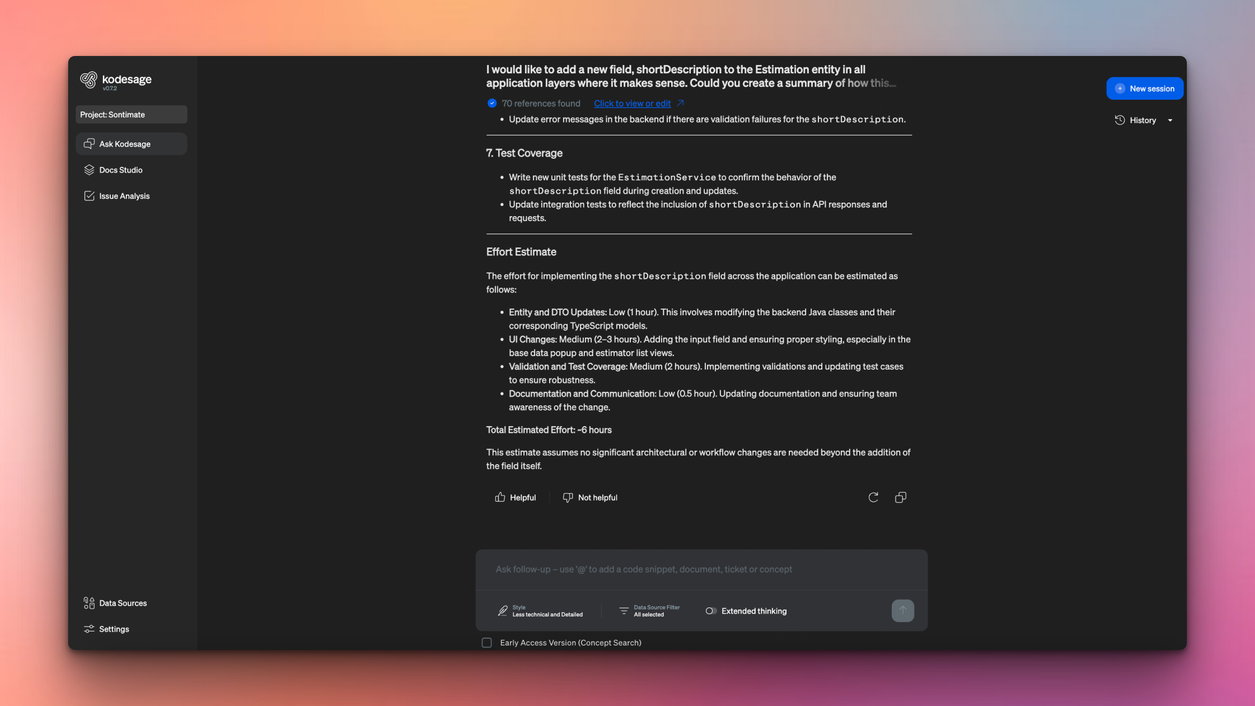
The goal is to improve scalability, enhance integration capabilities, and ensure maintainability. For example, a bank might modernize by breaking COBOL batch jobs into microservices, enabling faster processing, better scalability, and smoother integration with digital channels, all while reducing operational risk.
How to modernize COBOL
Step 1: Assess and document
The first step in any COBOL modernization effort is understanding what you already have. Many COBOL systems have grown over decades, often without complete or up-to-date documentation. Start by inventorying all COBOL programs, copybooks, batch jobs, and JCL processes.
Next, identify architectural relationships, data flows, shared data files, databases, and external systems. This step helps uncover hidden coupling that could introduce risk during change.
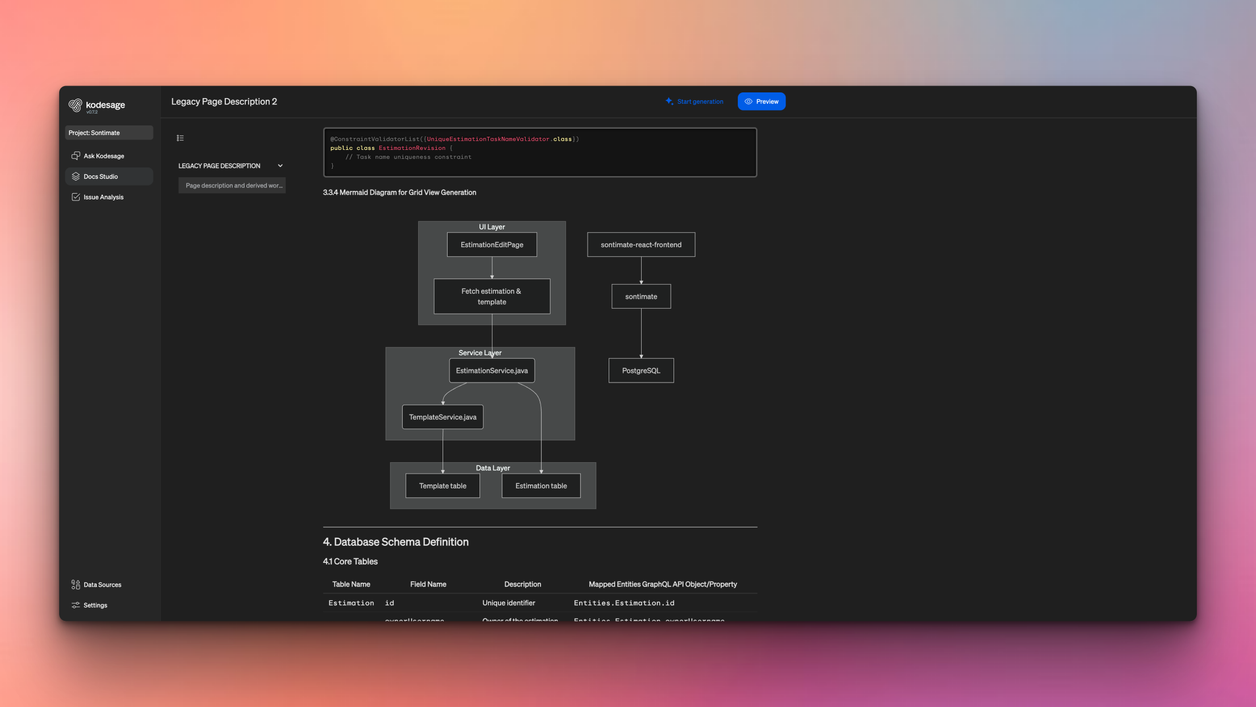
Then assess code quality, size, and stability. Not all components need immediate modernization. Some are stable and low risk, while others are fragile or frequently modified. Knowing the difference helps teams prioritize where modernization will deliver the most value.
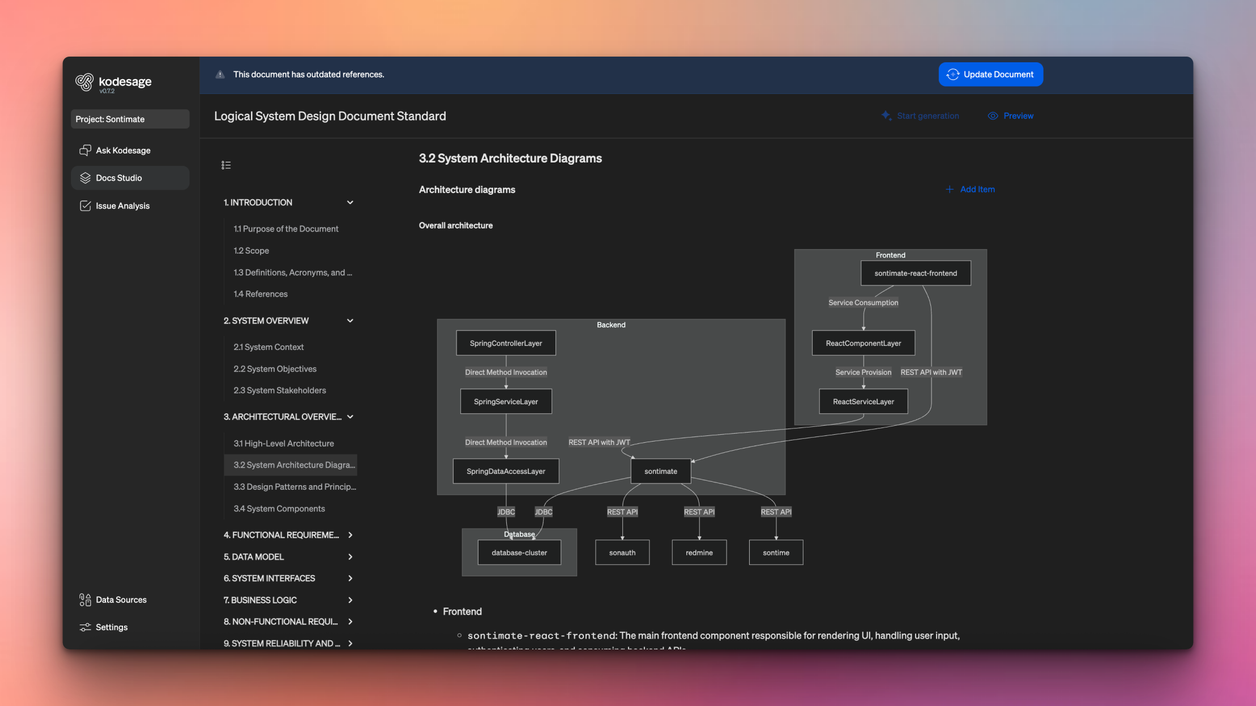
Kodesage supports this phase by automatically mapping COBOL dependencies and generating visual diagrams of how programs, copybooks, and JCL jobs interact. These diagrams make complex systems easier to understand and safer to change.
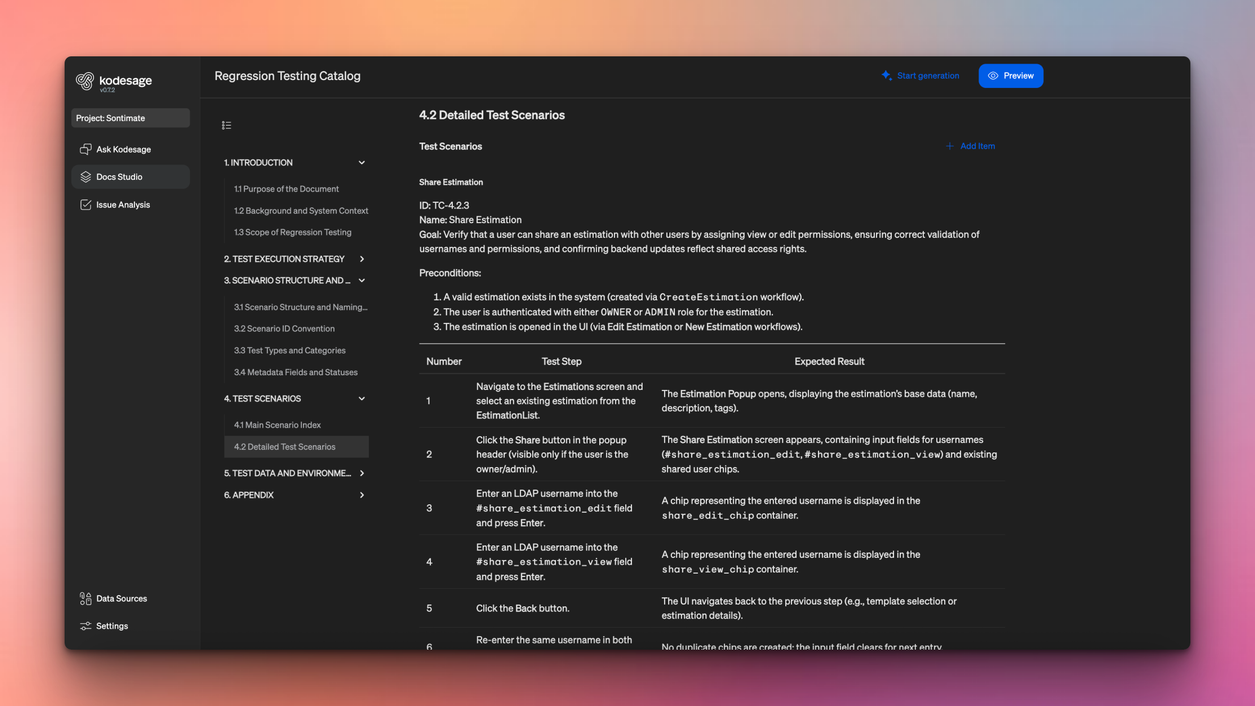
If test coverage is limited or does not meet audit requirements, Kodesage can also help generate retroactive tests. This ensures that documentation and testing stay aligned, reducing risk while bringing legacy systems closer to modern quality and compliance standards.
Step 2: Define modernization goals and architecture
Once you understand your system, decide what you want to achieve. Are you trying to reduce maintenance costs? Enable API access for mobile or web applications? Move workloads to the cloud? Your goals will shape every decision that follows.
Next, choose a target architecture. You might keep some COBOL components in a distributed setup, adopt a hybrid approach that mixes legacy and modern systems, or break monolithic applications into microservices. There's no single right answer; it depends on your business needs and risk tolerance.
Set clear success metrics early. Define KPIs like system uptime, transaction speed, and cost per transaction. Establish SLAs that reflect business requirements. These benchmarks help you measure progress and justify the investment.
Making these decisions without clear system visibility is risky. Kodesage generates a living knowledge base that is built of your entire codebase, your ticketing systems and internal knowledge bases, and other relevant sources connected. This knowledge base serves as a robust context layer for the LLM models used by the platform. Even though the vast majority of the process is achieved using connected data sources, there is great value in capturing power-user workflows upfront. This is labelled as Auto-consultancy by Kodesage. These daily routines of power-users are automatically captured, ensuring that COBOL specific domain understanding is added to the knowledge base.
This robust context ensure that all components and their interactions are correctly captured. Empowered with this knowledge, the target architecture can be defined with high confidence, and goals are fully aligned with both technical realities and business objectives.
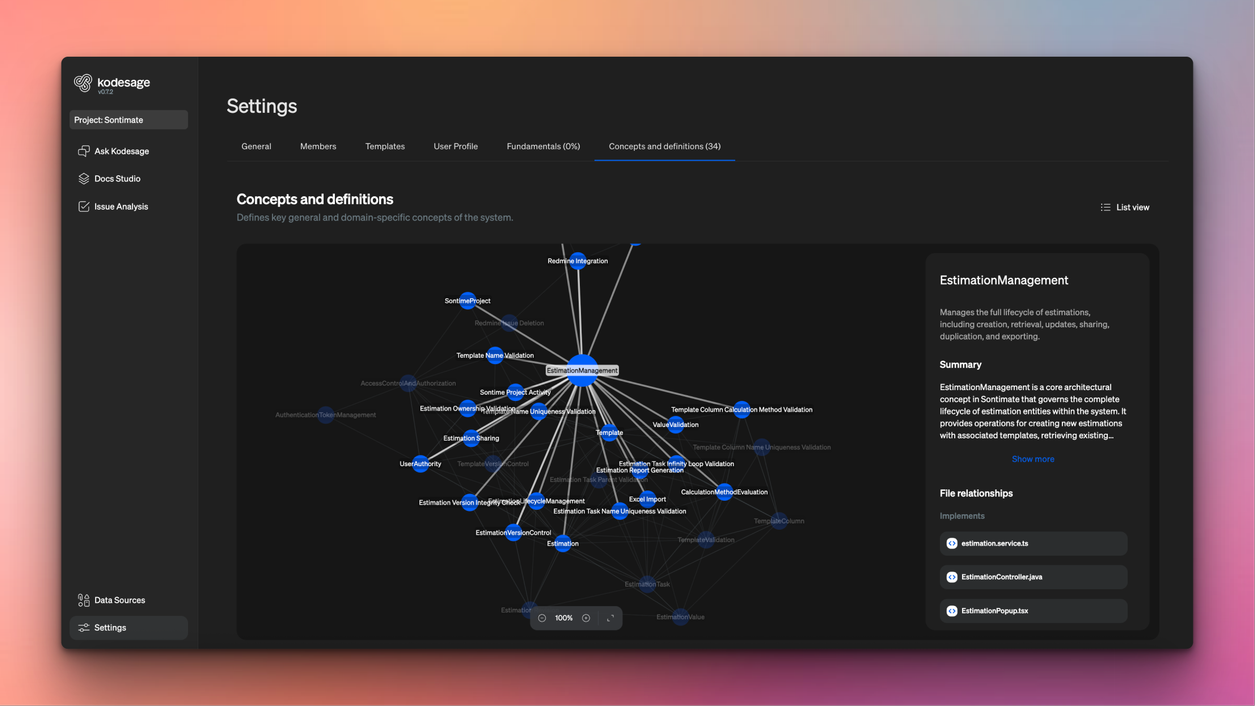
Step 3: Select Modernization Approach
When selecting a modernization approach, compare the three main strategies. Each differs in cost, risk, and time to value.
- Rehosting involves moving the COBOL application to a new environment with minimal code changes. It is often the fastest and most cost-effective option, but it offers limited scalability and long-term flexibility.
- Replatforming migrates the application to a new platform with targeted adjustments. This approach improves scalability and integration options but requires more time and effort than rehosting.
- Refactoring redesigns the application to meet modern architectural standards. It carries the highest cost and risk, but it delivers the greatest flexibility and long-term benefits.
The right approach depends on business goals and system criticality. Mission-critical systems often benefit from gradual modernization (phased approach) or rehosting, while less critical applications may be better candidates for deeper refactoring.
Step 4: Execute modernization
This is where planning meets action. Start by refactoring or migrating code using automated conversion tools where possible. Focus on decoupling business logic from presentation and data access layers. This separation makes systems easier to change and maintain over time. Kodesage can support engineering teams with the execution of code conversion. It also provides an IDE integration, which enables engineers to leverage the help of the platform while executing conversions.
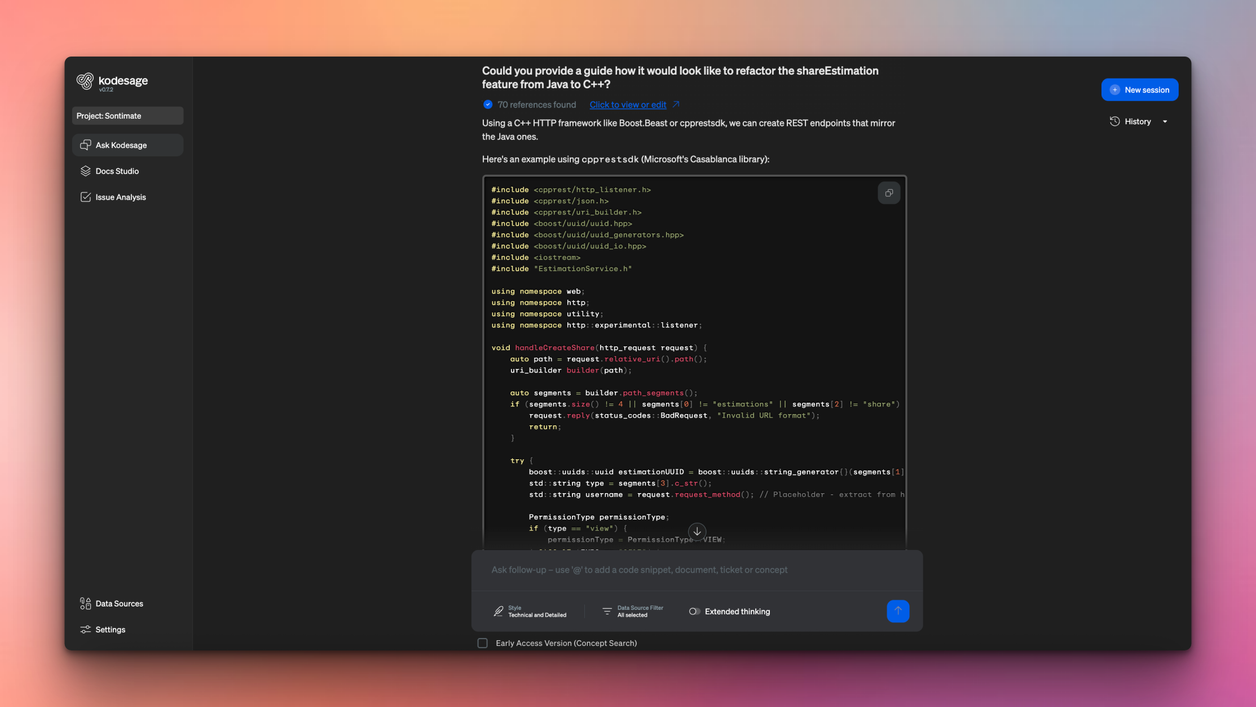
Modernize data access next. Many COBOL systems rely on flat-file I/O, which limits scalability and integration. Replacing these patterns with database services or REST APIs enables real-time processing and smoother interaction with modern applications.
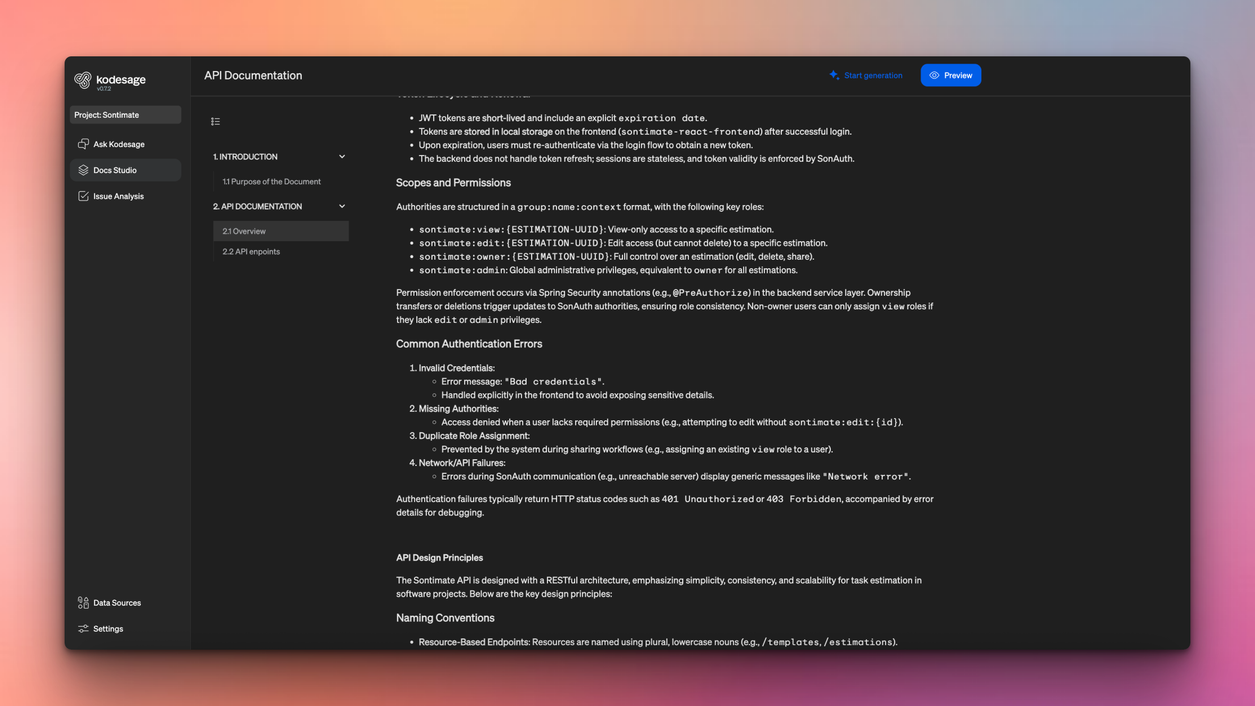
As modernization progresses, introduce new integration patterns. Expose COBOL business logic through APIs or connect systems using message queues. These approaches allow legacy systems to work with modern platforms without requiring a full rewrite. Kodesage's docs studio already comes with pre-built API documentation templates. These templates have detailed prompts configured by Kodesage, ensuring that APIs are fully documented, and all endpoints captured.
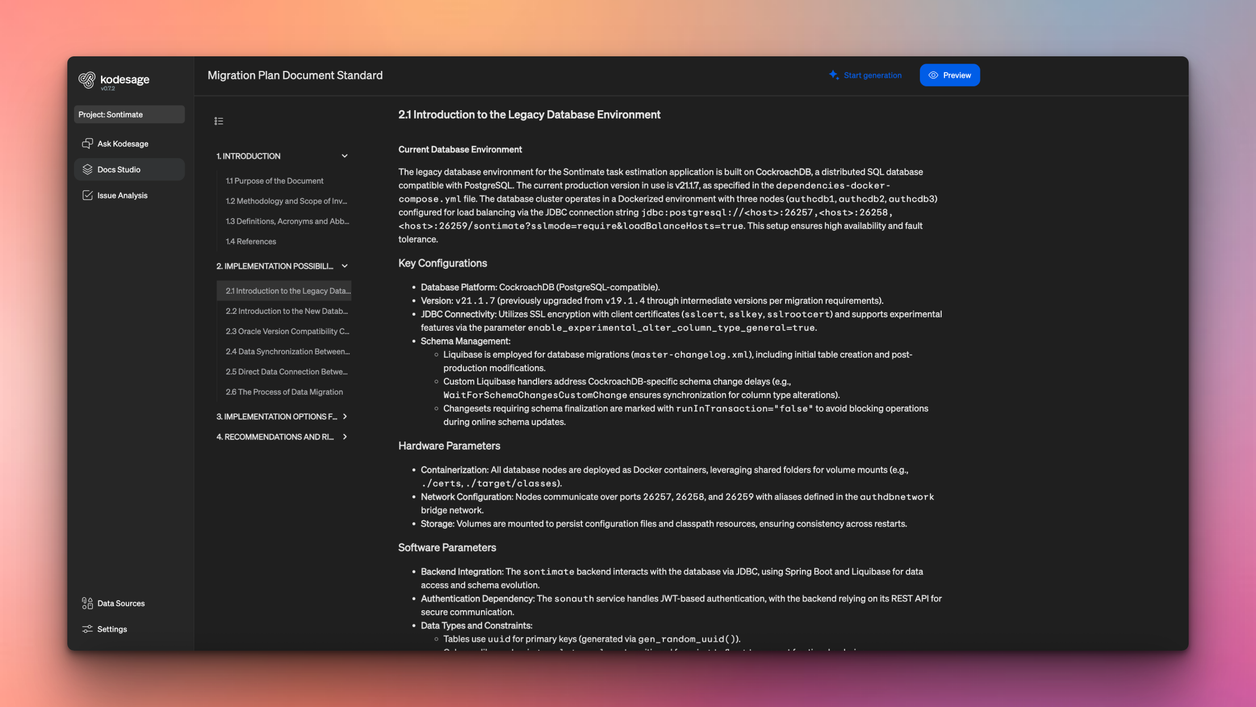
One of the biggest challenges at this stage is maintaining consistency. Critical system knowledge often lives across code comments, ticket histories, databases, and institutional memory. When this context is fragmented, migration teams risk missing important business rules.
Platforms like Kodesage address this by consolidating information from codebases, ticketing systems, databases, and documentation into one knowledge base. This standardized view of system logic helps teams generate the previously mentioned migration guides. These guides are closely reviewed by senior architects, and provide detailed context for LLMs to work from.
Step 5: Automate, test, and optimize
Modernization does not stop once code is migrated or refactored. To reduce long-term risk, teams need repeatable processes that keep systems stable as changes continue. This starts with introducing version control, CI/CD pipelines, and automated test suites to replace manual deployment and validation.
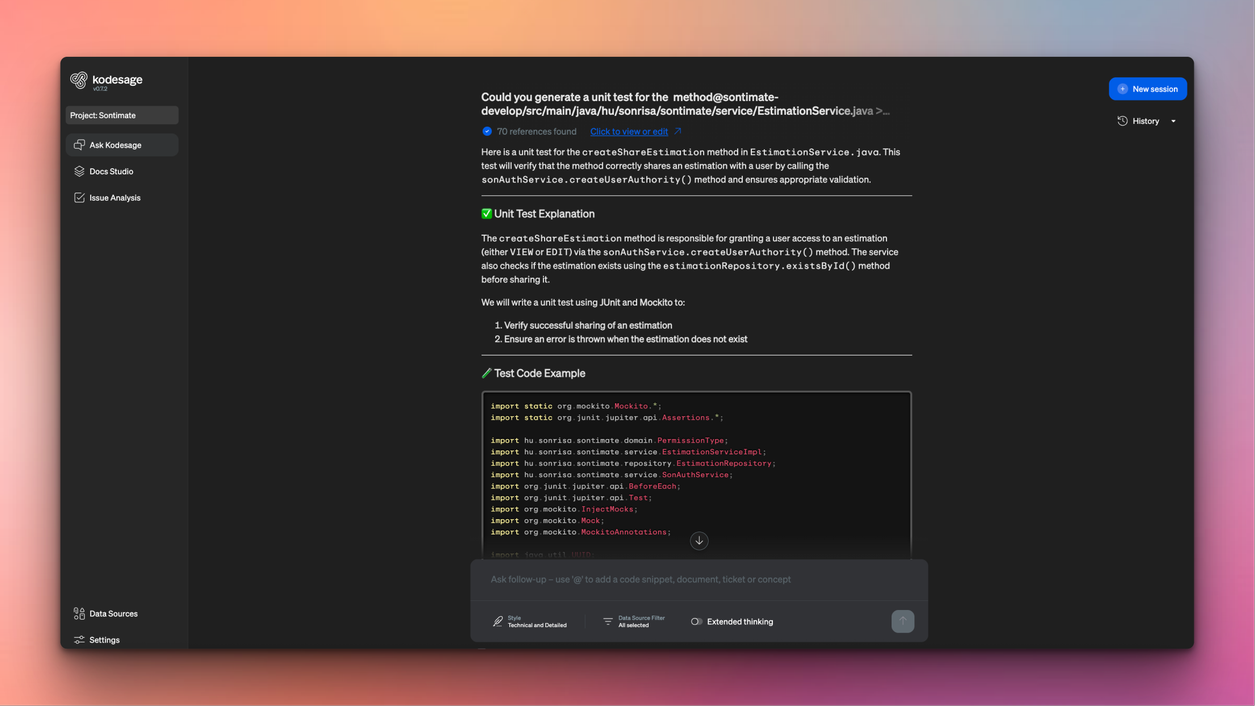
Testing is critical at this stage. Teams must confirm that core business logic behaves exactly as before. Unit, regression, and integration tests help catch subtle issues that could affect downstream systems or financial calculations. Containerizing workloads also improves portability, making it easier to run COBOL-based services consistently across environments.
Kodesage supports this phase by keeping documentation up to date as refactoring progresses, ensuring changes remain traceable and audit-ready. It can also help increase test coverage by automatically generating unit and regression tests from existing code. This gives teams greater confidence as they optimize performance and scale modernized systems.
Step 6: Deploy and evolve
Once automation and testing are in place, teams can deploy modernized components with greater confidence. Most organizations roll out changes in phases, starting with non-critical modules and expanding gradually. This approach reduces risk while allowing teams to monitor performance, stability, and cost improvements in real production environments.
At this stage, modernization becomes continuous. Teams refine deployments, adjust architectures, and train developers, operations, and support staff on the new environment. Feedback from production usage informs further improvements and optimization.
In parallel, legacy COBOL systems often remain in production during phased modernization and still require ongoing support. Maintaining these systems alongside new development can strain teams and slow progress.
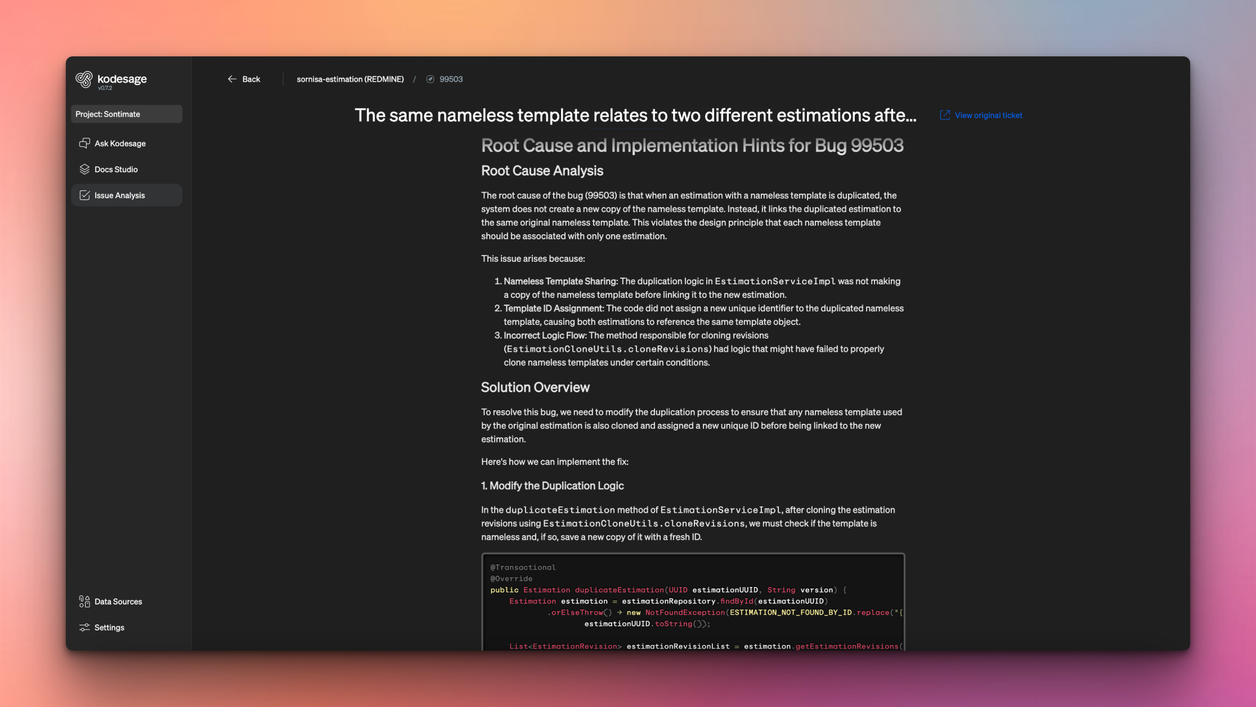
Kodesage supports this transition by keeping system knowledge accessible through AI-powered search and continuously updated documentation. It also improves production support by analyzing every issue ticket and generating fix recommendations, including code-level guidance.
Product managers and business analysts working out new features can also plan and validate ideas independently using Ask Kodesage. They can get detailed step-by-step guides for adding features, and can generate technical assessments without involving senior engineers who are preparing for the technical planning of the modernization. This new approach of having Kodesage assisting as a senior engineer can significantly accelerate discovery cycles.
This allows teams to support legacy systems with fewer resources, freeing more capacity to evolve the modernized platform.
COBOL modernization strategies and their trade-offs
There is no single path to COBOL modernization. Most organizations choose a strategy based on how quickly they need results, how much risk they can tolerate, and how deeply they want to modernize the system.
Strategy | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Rehosting | Shifts COBOL applications onto modern infrastructure, such as cloud platforms or Linux environments, with minimal disruption | Improves operational flexibility but leaves legacy code structures and user interfaces largely unchanged |
Refactoring | Transforms COBOL logic into modern languages, making systems easier to maintain and extend | Demands strong domain knowledge and rigorous testing to avoid breaking critical business rules |
Replatforming | Runs existing COBOL code on updated runtimes or compilers | Delivers modest modernization gains while still limiting architectural flexibility |
Rewriting | Rebuilds applications using a modern technology stack from the ground up | Offers the cleanest result but comes with higher costs, longer timelines, and greater delivery risk |
Replacement | Swaps custom COBOL systems for SaaS or packaged solutions | Accelerates delivery but may struggle to replicate highly specialized or regulated workflows |
In practice, many teams combine approaches, modernizing high-value components first while managing risk across the broader system.
Common challenges in COBOL modernization
- Complexity of legacy codebases: COBOL systems are often large, tightly integrated, and poorly documented, making them difficult to understand, refactor, or migrate without disrupting critical business processes.
- Skill shortage and knowledge loss: Many experienced COBOL developers are retiring, creating a gap in expertise. This loss of knowledge makes maintaining or modernizing legacy systems more challenging and time-consuming.
- Data migration and integrity risks: Migrating data from COBOL-based systems to new platforms carries the risk of data corruption or inconsistency, potentially affecting business operations and requiring careful validation.
- User and stakeholder resistance: Employees and stakeholders may resist change due to their familiarity with legacy systems. Overcoming this resistance is crucial for a smooth transition and adoption of modern solutions.
- High initial cost and tooling investment: COBOL modernization often requires significant upfront investment in tools, training, and resources, which can strain budgets, especially when long-term ROI is not immediately visible.
Best practices for COBOL modernization
The following best practices help reduce risk while maximizing long-term value.
- Plan and prioritize with precision: Start by identifying which systems and components deliver the most business value or carry the highest risk. Clear prioritization prevents wasted effort and keeps modernization aligned with business goals.
- Adopt an incremental, phased approach: Break modernization into manageable phases rather than attempting a full replacement at once. This reduces disruption, allows continuous learning, and delivers value earlier.
- Modernize tooling and DevOps from day one: Introduce version control, automated testing, and CI/CD pipelines early. These foundations improve quality, speed, and confidence throughout the modernization journey.
- Involve stakeholders and document early: Engage business users, operations, and compliance teams from the start. Clear documentation ensures shared understanding and reduces resistance to change.
- Leverage AI-powered legacy knowledge tools: Platforms like Kodesage help capture business logic, dependencies, and system behavior, reducing reliance on scarce experts and supporting safer decision-making.
- Consider all options before choosing: Carefully evaluate different modernization strategies, whether replatforming, refactoring, or rehosting. Choosing the right approach depends on your business goals, system criticality, and resource availability.
How Kodesage supports seamless COBOL modernization
Kodesage is designed to streamline the transition from legacy COBOL systems to modern platforms, offering powerful tools that reduce migration complexity and risk:
- AI-powered modernization: Kodesage analyzes millions of lines of COBOL and JCL code, identifying system structure and dependencies. This process saves up to 60% of discovery time, enabling faster and more accurate modernization planning.
- Automated documentation: Kodesage automatically generates and updates comprehensive documentation, including data lineage maps and dependency charts. This reduces 80% of the manual work required to keep documentation current and prevents valuable knowledge loss.
- System mapping and visualization: Kodesage visualizes control flow and data dependencies, isolating callable logic for refactoring or API enablement, ensuring smooth integration with modern systems.
- Accelerated onboarding: New developers can quickly understand legacy code through Kodesage’s natural language interface and contextual documentation, reducing the learning curve from months to weeks
- Enterprise-ready deployment: Kodesage supports on-premise and air-gapped environments, providing detailed system blueprints while ensuring compliance and safeguarding sensitive data during modernization
Modernize COBOL systems seamlessly with Kodesage
COBOL modernization is important for reducing risk, improving agility, and keeping core systems reliable as business demands change. The challenge is modernizing without breaking the logic that still runs critical operations.
Kodesage makes this possible by giving teams clear visibility into legacy COBOL systems. Automated documentation, system mapping, and actionable insights help teams modernize safely and make confident decisions at every step.
See how Kodesage helps organizations modernize COBOL systems while protecting what matters most. Request a demo today.
Why choose Kodesage?

Deep Legacy Code Intelligence
Kodesage supports legacy stacks like Oracle Forms, COBOL, PowerBuilder, SAP, PL/SQL, and also modern stacks.

Secure On-premise Deployment
Single tenant application, offering both VPC and fully on-premise deployments meeting the strictest security requirements.

Living Knowledge Base
Connect to the entire codebase, issue ticketing systems like Jira, databases, tests, wikis like Confluence and upload documents.

Automated Documentation
AI generated software documentation that is always up to date with a pre-built and editable document template library.

Regression Test Automation
Automate regression and unit test coverage, accelerate releases and ensure traceability for future audits.

AI-powered Issue Ticket Analysis
Native integration to systems like Jira, and AI-generated fix recommendations for tickets.
Start transforming your legacy systems
With Kodesage teams maintain legacy projects more efficiently, and modernize faster.
See it in action today.
